Centre for Geotechnical Science and Engineering
Numerical study of jointed rock slope instability on a combined FEM and DDA method
Key Researchers: Shanyong Wang, Stephen Fityus, Anna Giacomini
PROBLEM DESCRIPTION
In an increasingly crowded and overpopulated world, the growing demand for mineral resources, urbanisation and transport infrastructure to facilitate them, requires reliable engineering solution to increasingly challenging problems, our growing need for minerals is driving bigger and deeper open pits with more extreme rock slopes. Urban areas are extending into areas threatened by slope instability and landslides. And in many cases, the only way to traverse congested cities and heavily utilised ground is to go under it. Many steep natural and manmade slopes are prone to instability, and where these slopes comprise fractured rock, effective hazard assessment and mitigation requires reliable tools for rock mass stability assessment. These same tools are also useful for the reliable assessment of underground openings in fractured rock, such as tunnels and for motorways, railways and mass transit systems.
The objective of this research is to develop a novel whole-process method by combining FEM and DDA to model the nonlinear deformation and failure behaviors of fractured rock slopes and rock masses, and to provide tools to simulate the transformation of rock materials from continua to discontinua as they undergo loading-induced fracturing. This will be achieved through a combination of experimental and theoretical research. The developed method is expected to be able to characterize mechanical discontinuities as well as to simulate progressive failure processes and instantaneous collapse in rock masses.
SCIENTIFIC AND ENGINEERING APPROACHES
- Characterize the behavior of continuous sub-domains and mechanical discontinuities within the same model.
- Model small deformation including fracture initiation and growth.
- Capture large displacement including body movement and mechanical contact.
- Achieve the automatic transformation of rock materials from a continuum to a discontinuum.
- Realize the parallel solution for the combined FEM and DDA method on PC by using the CPU-GPU heterogeneous computing method and in the cluster parallel environment by using the Open MP multi thread library.
APPLICATIONS
- Australian society will benefit from the new numerical tools to facilitate more reliable assessment of risks associated with instability in rock slopes. Australian mining and transport infrastructure will benefit from more reliable design of underground openings.
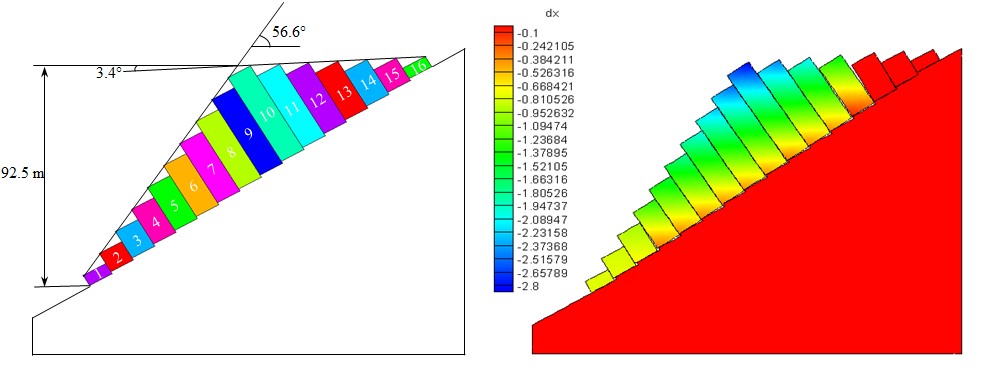
Figure 1: Combined REM and DAA model set up
The University of Newcastle acknowledges the traditional custodians of the lands within our footprint areas: Awabakal, Darkinjung, Biripai, Worimi, Wonnarua, and Eora Nations. We also pay respect to the wisdom of our Elders past and present.
